Laser metrology systems have important applications in a variety of industries, including semiconductors, the medical sector, aerospace and automotive industries. The semiconductor manufacturing process uses the laser metrology technique for accurate optical measurements. There are various techniques in laser metrology to measure the physical dimensions of different parts and sub-parts.
The use of diffractive optics can boost the efficiency and performance of a laser metrology system. While various industries use lasers for different purposes and applications, a common factor is that they all require modified laser beams that exhibit a uniform intensity distribution pattern. Laser metrology employs diffractive optical elements or DOEs as beam shapers to modify the intensity profile of the input beams and convert it into a hat output intensity profile. A tophat beam has a uniform focused spot and well-defined shape and size. The beam profile similar to a flat-top or top hat, hence, the name “top-hat beam”.
Diffractive Optics in Laser Metrology
Diffractive optical elements offer various advantages in laser metrology applications, including:
- High Precision
The use of diffractive optics ensures very high angular accuracy and tight tolerances that are necessary for accurate measurements.
- Customization
Diffractive optical elements can be customized to meet precise requirements regarding the shape and size of the output laser beam. Therefore, these optical components can shape the incident laser beam profile differently, from a top-hat or flat-top intensity profile to an array of spots at desired seperations.
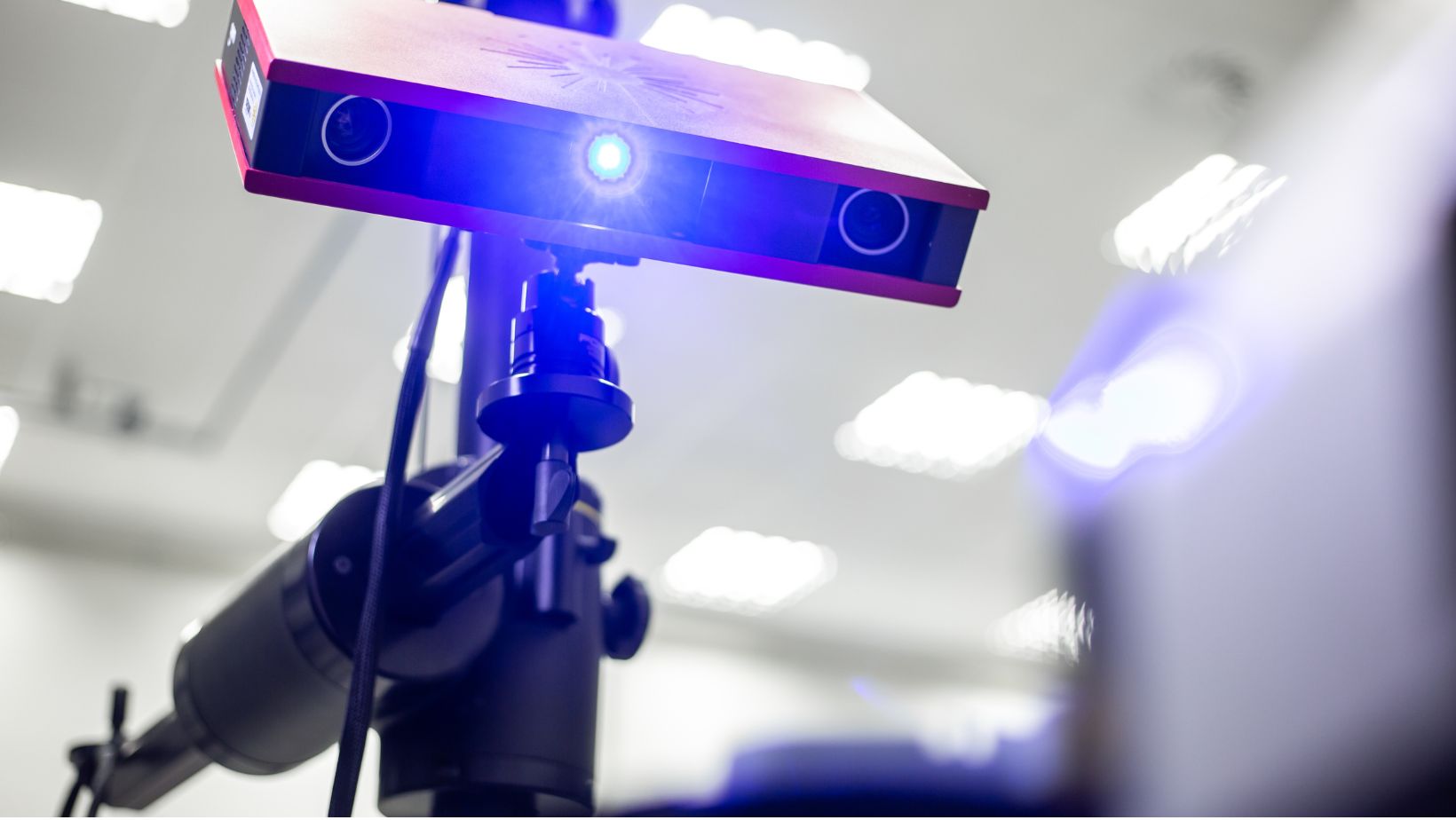

- Easy-to-integrate:
DOEs are flat windows, easy to integrate into different optical systems. Therefore, different industries can utilize DOEs in their laser applications.
- Durability:
Lastly, DOEs offer high durability and high stability, which makes diffractive optics an absolute solution for laser metrology systems.
Applications of Laser Metrology
Here, we will discuss three major industries that rely on laser metrology for different applications, such as the semiconductor industry, the medical sector, and the aerospace and automotive industry.
Semiconductor Industry:
In the semiconductor industry, laser metrology plays a key role in the fabrication or characterization of complicated geometries and microstructures (Example: Optical Critical Dimension or OCD). The semiconductor industry aims to meet high precision and throughput by using laser metrology.
Medical Sector:
Laser metrology has critical applications in the production of medical devices. Laser metrology has improved the efficiency of the medical sector by providing accurate measurements for a variety of physical parameters.
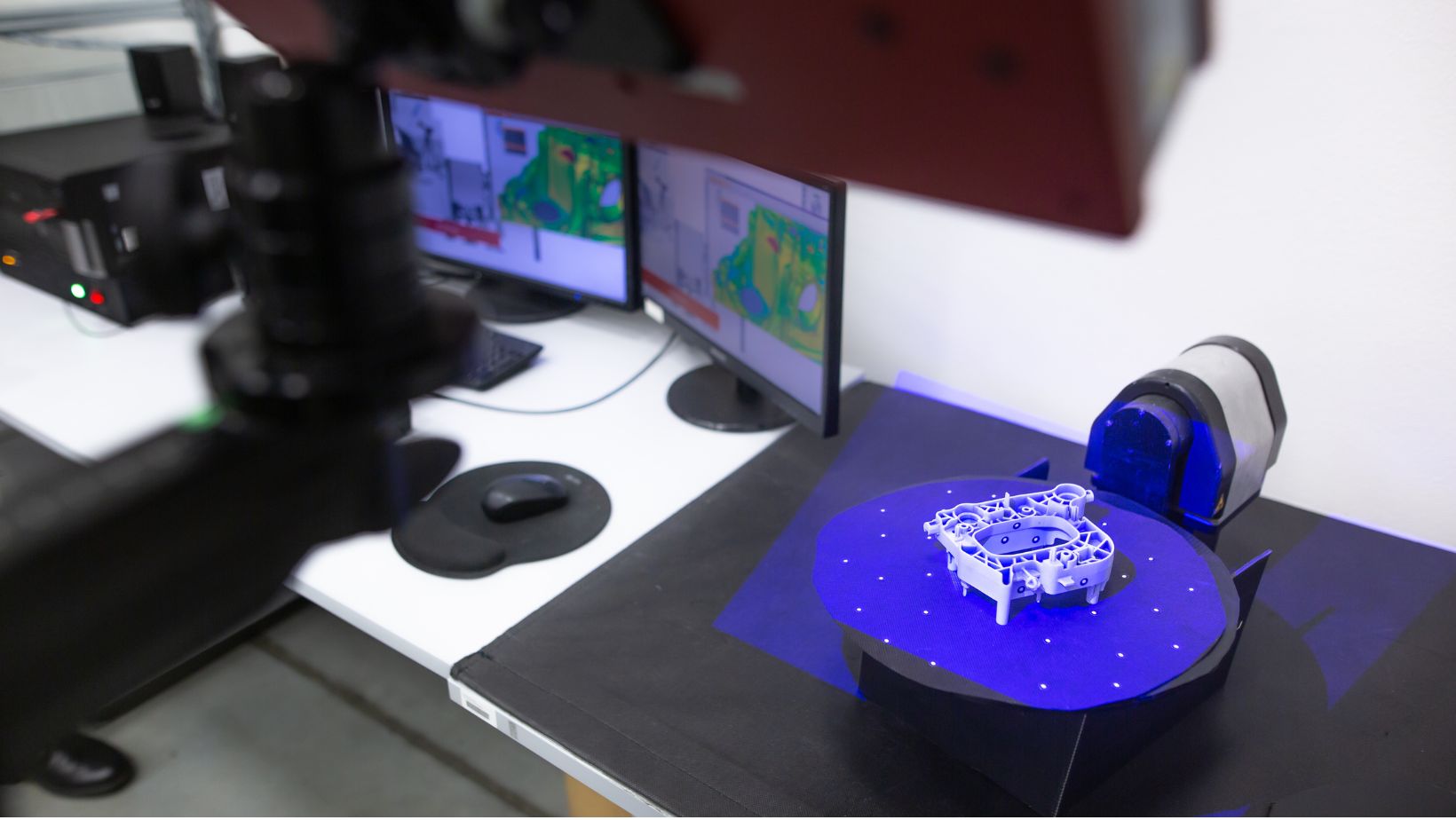
Aerospace and Automotive Industry:
This industry uses laser metrology to precisely measure critical components and maintain traceability with high standards.
Challenges in Laser Metrology
The major challenge that laser metrology encounters is that it requires advanced components to ensure accuracy and reduce noise. Advanced optical solutions are required for high-resolution measurements, using extreme ultraviolet lithography. The use of elongated-focus DOEs in this laser metrology will increase the detection range and improve resolution.